President Donald Trump has slapped dozens of America’s trading partners with new tariff rates, but Australia’s exports to the United States have been spared a hike.
Most of these new tariff hikes were first announced in April when Trump slapped a minimum 10 percent levy on goods from almost every country in the world, citing unfair trade practices and US deficits.
However, Washington then postponed implementation, amid frantic series of negotiations, alongside announcements of new duties and deals with some partners.
The new tariffs are due to take effect on 7 August.
A spokesperson for Trade Minister Don Farrell said Australia had been left the “best possible position” after it was revealed the 10 per cent baseline tariff would not be increased.
“While we remain in the best possible position under the United States’ new tariff regime, we will continue to advocate for the removal of all tariffs in line with our free-trade agreement.”
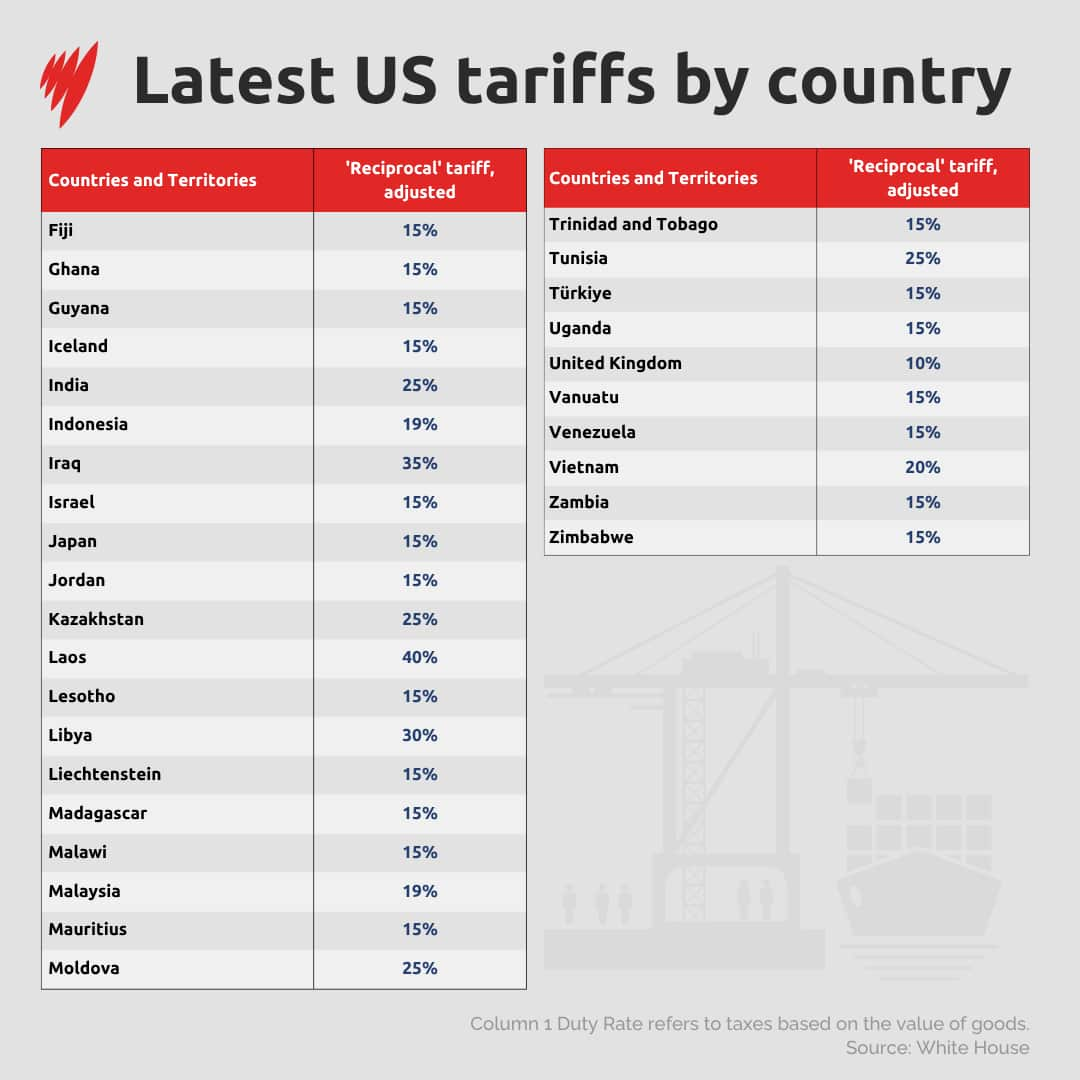
Exports from Australia’s neighbours — New Zealand, Fiji, and Papua New Guinea — were hit with greater 15 per cent tariff.
And those from other countries face an ever higher rate, including India (25 per cent) South Africa (35 per cent) and Syria (41 per cent).
There was a frantic series of negotiations ahead of the US’ self-imposed deadline of 1 August, alongside announcements of new duties and deals with some partners, including the European Union. Other trading partners had no opportunity to negotiate with the Trump administration.
In a statement, the White House said the so-called “reciprocal tariffs” were increased on countries that failed to engage in negotiations with the US or to take adequate steps to align sufficiently on economic and national security matters”.
The order said that goods from all other countries not listed in an annex would be subject to a 10 per cent US tariff rate.
A US official told reporters that more trade deals were yet to be announced as Trump’s higher “reciprocal” tariff rates were set to take effect.
“We have some deals,” the official said. “And I don’t want to get ahead of the President of the United States in announcing those deals.”
Australia has yet to sign a formal trade deal with the US following the introduction of the tariffs.
List of US tariffs
Some countries face higher tariffs but were not included in the list published on Friday AEST.
That includes Canada (35 per cent), with Trump this week saying that Canadian government’s move to recognise Palestinian statehood would make a trade deal “very hard”.
Brazil was listed as 10 per cent, but an additional 40 per cent tariff has been applied. However, some sectors — including aircraft and energy — have been spared.
Mexico has been granted a 90-day reprieve from higher tariffs of 30 per cent to provide more time to negotiate a broader trade pact.
China was also excluded. It faces a 12 August deadline for a deal, after which duties could bounce back to higher levels if one isn’t reached.
Source: SBS News
There had been speculation that Australian goods would be hit with a higher levy, given Prime Minister Anthony Albanese has so far failed to secure a face-to-face meeting with the president and after Trump on Tuesday said he was planning a new tariff “for the world” in the 15-20 per cent range.
Australia will keep pushing for a full exemption from the US tariffs, with Farrell inviting US Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick to continue discussions.
But it’s unclear if the government will be successful.
The US has complained to Australia about non-tariff trade barriers including longstanding restrictions on beef following a prior outbreak of mad cow disease, and the federal government’s decision to lift restrictions on US beef imports was hailed as a victory by Trump.
A tariff (or import duty) is a tax imposed on foreign goods imported into a country.
Tariffs aren’t paid by the foreign countries they target. Instead, they’re charged to the buyer of those goods and the money goes to — in this case — the US treasury.